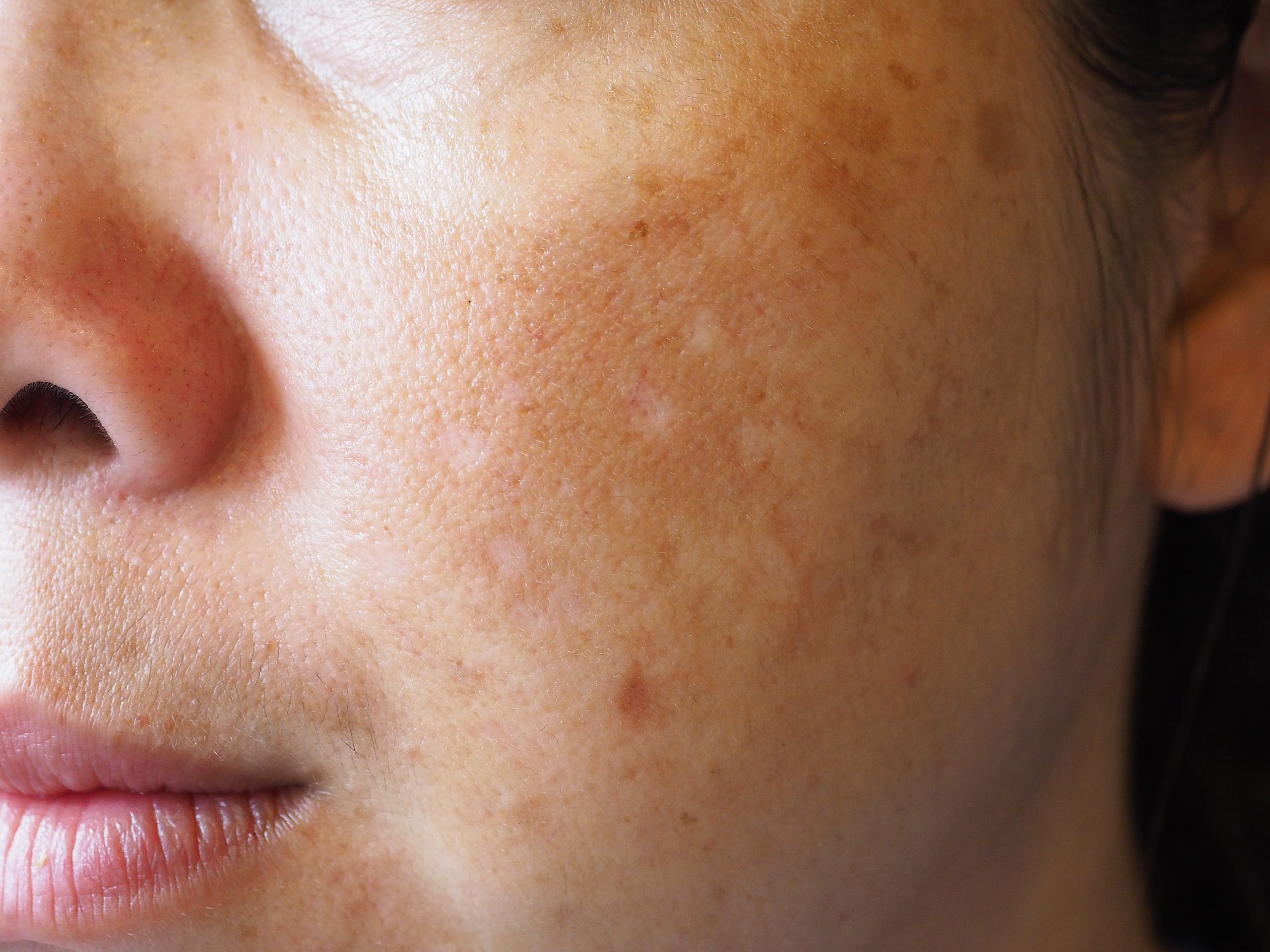
What is melasma?
Melanin is produced by pigment cells in the skin which gives the skin its color and helps protect it from the harmful effects of sunlight. Melasma is a buildup of melanin which results in grey to brown patches most commonly on the cheeks, forehead, and chin. Although it can occur in both sexes in people of all ethnicities, it is more often seen in women and those with darker complexions. It is common among women living in areas with a lot of sunlight, particularly in Hispanics, Asians, and African Americans. The patches usually develop slowly and symmetrically, and can last for many years. There is often worsening in the summer and some improvement during the winter.
What is melasma caused by?
Melasma has a variety of causes including genetic factors, pregnancy, use of estrogen containing birth control, hormone treatments, and exposure to sunlight. Recently, some evidence has come out that melasma can also be stress related.
How can I prevent melasma from developing?
Melasma is often difficult to treat. The goals of treatment include preventing it from spreading and lightening existing spots. Regular use of a daily, broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential. The idea is that protection from sunlight reduces melanin synthesis and helps to remove existing pigment. Broad-spectrum sunscreen with 30 SPF or higher should be applied daily throughout the year to lower the chance of re-activating the pigment producing cells. Even small amounts of sun exposure on a cloudy day can stimulate pigment production.
How does hydroquinone treat melasma?
Hydroquinone works by preventing the production of melanin. It is safe and effective to treat melasma and other forms of excess pigmentation. Used with broad-spectrum sunscreen, it works over several months to lighten skin. It has to be used at the same time as sunscreen, otherwise new pigment will be formed just as fast as the old pigment is dissolved. It is safe and well tolerated in the majority of women when used for less than 12 months. Most side effects are due to misuse, excessive use, and the application of other medications at the same time. Importantly, there is a possibility of something called ochronosis, which is permanent blue-black pigmentation resulting from long-term application. However, this side effect is rare and is almost always seen in women who use hydroquinone for more than 1 year and at very high concentrations.